The first of December is Antarctica Day – and since the day and the world seem a bit gloomy today, I thought I’d share a 100% omicron-free Antarctic penguin-party with you.
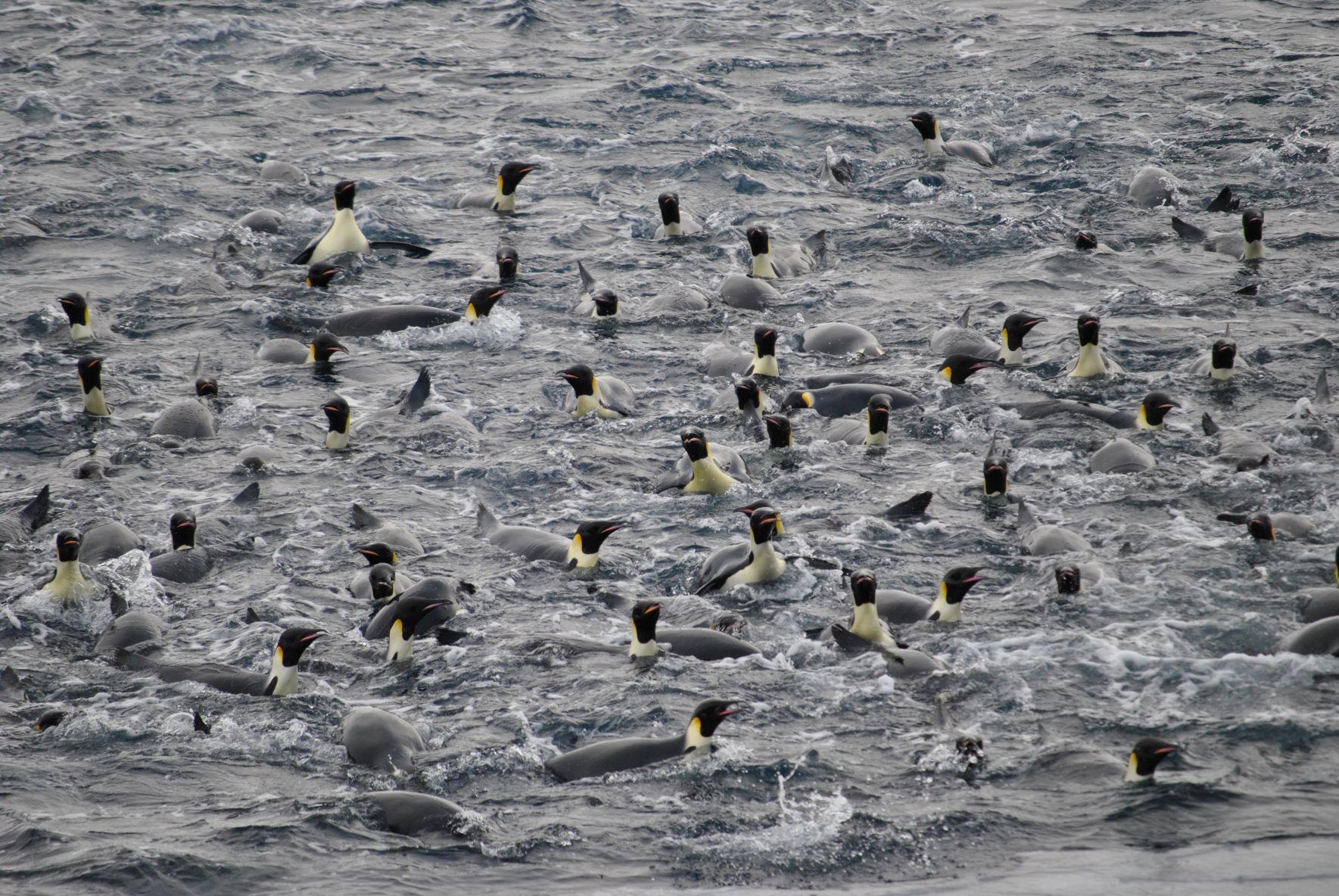


The first of December is Antarctica Day – and since the day and the world seem a bit gloomy today, I thought I’d share a 100% omicron-free Antarctic penguin-party with you.

… for my colleague, mentor, ex-supervisor, favorite feminist, and friend Prof. Anna Wåhlin who just got selected “rådsprofessor” (~council professor) by the Swedish research council! Along with the honor comes a grant of 50 MSeK (5 Million Euros) to be used in a research project on ocean – ice shelf processes in the Amundsen Sea during the next ten years – I’m sure Ran (the Swedish autonomous (unmanned) research submarine) will get to go on many nerve-wracking excursions under the ice shelves and that she will bring back a lot of exciting data and discoveries! Congratulations Anna – and thank you for involving me in your work – it is so much fun to discuss science with you!

… is not a question anymore. All our students learn Python, starting the day they enter the university (and even before), and when teaching you are expected to integrate Python and programming whenever possible.
Of course, it makes sense for the university to promote the use of a free, open-source software rather than a commercial product like Matlab, but for all of us old (and not so old) lecturers at the university who – like me – have done your data analysis and plotting since the beginning of time in Matlab, it is not an easy switch.
I took a Python course more than a year ago, and I’ve done a bit of Python here and there, but for a long time now, it has been one of those uncomfortable “have-to-do” but “not-right-now” things that keep accumulating at the horizon. Until a month ago, when a twitter-thread by a colleague (Thanks, Angelica!) who had decided to take the step (and who enjoyed it!) finally got me to dive headfirst into the Python world… so, I read a Python – book (Python for Data analysis by W. McKinney) and set my mental default “program-to- open-when-time-for-science” to Python (or Jupyter, Python is a programming language, not a program). I did not go as far as to uninstall Matlab, but I’m only using it for emergencies…
I quickly realized that I’m Google-dependent – whenever I don’t know how to do something – Google is there to help, directing me to Stackoverflow or one of the thousands of Python tutorials that are available online. It seems like (almost) every question has been asked before – and that there is an army of Python-enthusiasts out there ready to answer and help*!
Now, Matlab and Python have much in common – it is not like I’m starting to learn programming from scratch. Maybe more like learning to speak Norwegian (rather than Chinese) when your mother tongue is Swedish? You understand what the Norwegians are saying (i.e. you can read and – at least roughly – understand code that others have written), but to write your own Norwegian text and to speak… hmmmm, not so easy! You quickly get used to all the small differences – like that you have to start counting on zero and not on one, and that you have to use # and not % to comment out lines – but get accustomed to all the different types of variables in Python, to build up a vocabulary of commands and to “think” in a python way, rather than “translating” your Matlab – way of doing things will take longer time.
I’ve lived more than a decade in Norway – but my children still laugh if I open my mouth and try to speak Norwegian… hopefully, it won’t take that long to be fluent in Python!
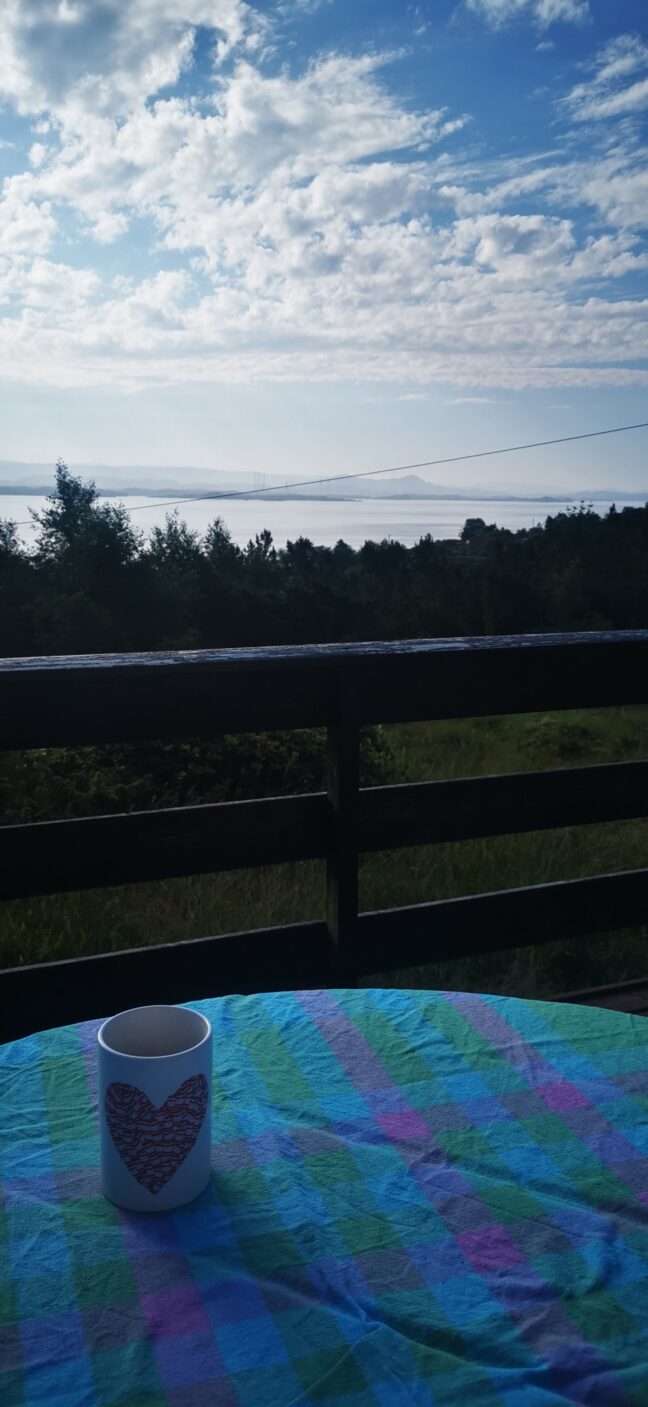

The Norwegian word “hytte” means cabin, and as a foreigner in Norway, you easily get the impression that *everyone* has (or has access to) a “hytte” (if not two or three). That is of course not true, but to “blend” in (end to enjoy lazy weekends away from home) my husband and I bought a “hytte” on an island not far from Bergen a few years ago.
With the kids away on scout camp this week, we took the opportunity to turn the hytte into “Hytte office”. With laptops, food, and an upgraded data deal with our mobile operator in the trunk we headed out to Øygarden earlier this week – and it’s amazing!
I do appreciate the changes in communication that the pandemic has forced upon us – from my “hytte office” I’ve participated in a Ph.D. defense in Paris (Congratulations, Ph.D. Lucie!), discussed figures and results from the Fimbul ice shelf with colleagues in Tromsø and checked in on what our seals in the Weddell Sea are up to… all while enjoying this wonderful view!

… it’s also a real treat to just step outside and munch a few blueberries (yes they are blue already!) while your Python script is munching away on the commands!
Have a nice summer!
… the flow of warm water into the Getz ice shelf cavity is reduced! Wonder why? Well, Ph.D. Nadine Steiger (who successfully defended her thesis yesterday! Yippie and congratulations, Dr. Nadine!) nicely explains it in a newly published paper:
Here’s a short version:
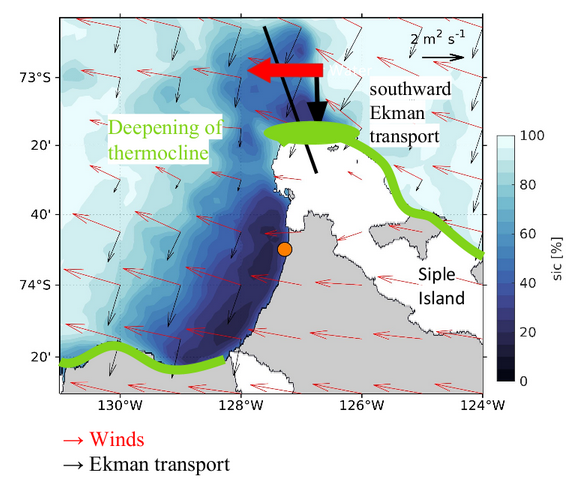
1) Eastward wind will (in the southern hemisphere) cause the surface water to move southward. (Oceanographers call this the “Ekman transport”). Water will hence pile up along the coast, along the green lines in the figure below.

2) When surface water piles up along the coast, it will press down the warmer water below (Oceanographers call this “coastal downwelling”)
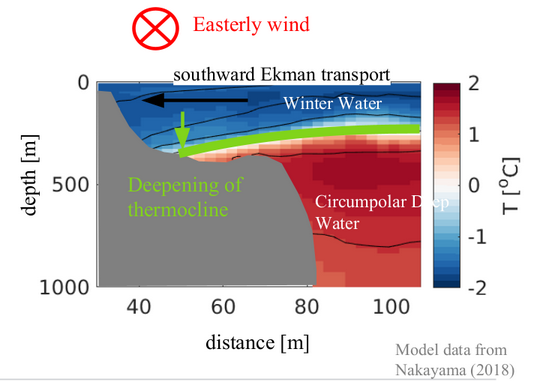
3) The disturbance (i.e. the signal with depressed warm water) will travel along the coast (Oceanographers would call this a coastally trapped, internal wave. The wave is “internal” because the signal is traveling on the interface between two water masses, not on the ocean surface) and reaches the western Getz ice front 3 days after the storm! The figure below shows the observed temperature& salinity in the vicinity of the ice front, and below you see the wind and sea ice concentration. Each time the temperature at depth drops (marked by green triangles) there has been a storm just before!
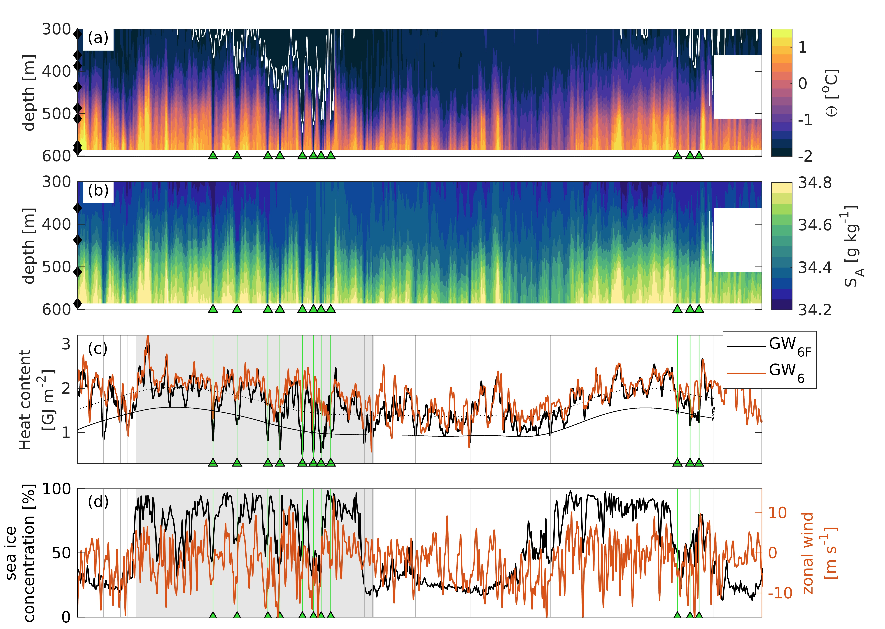
4) When the wave arrives at the ice front, two things happen. Firstly the thickness of the warm water layer is greatly reduced (see above) and, secondly, the current changes direction so that the flow at depth is aligned with the ice front rather than to enter the ice shelf cavity like it normally does.
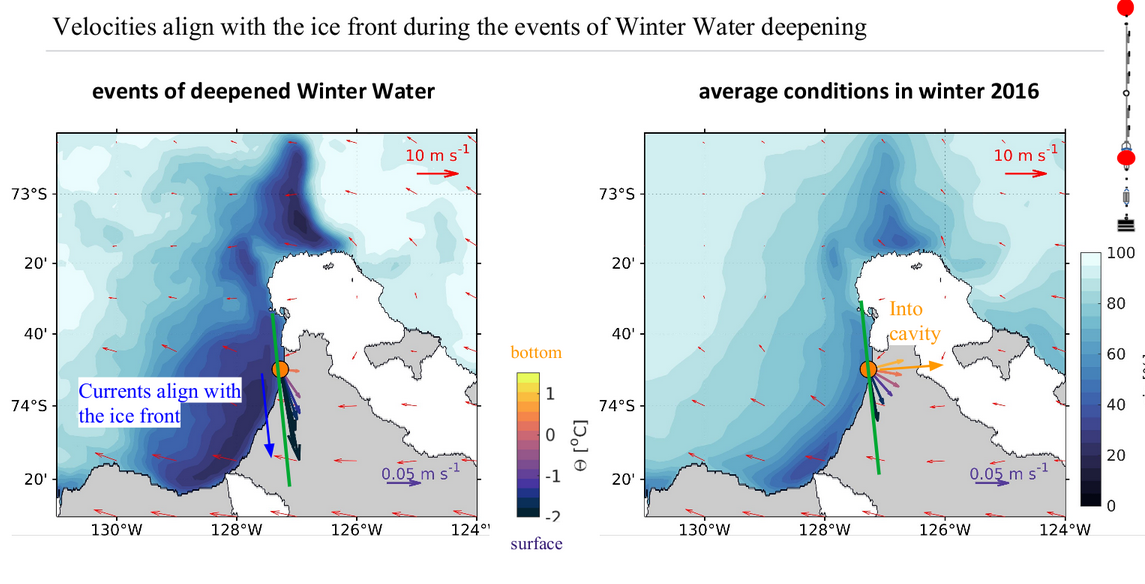
During the winter of 2016, this happened at least eight times – causing a reduction of the heat transport into the cavity by about 25%!
Well done, Dr. Steiger!!!

What a morning! Scrolling through the newly published list of funded projects from the Norwegian Research Council while sipping your breakfast tea and finding this:
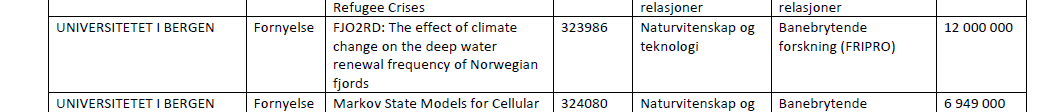
is even better than learning that Sweden qualified for the quarter-finals yesterday!
… and further down on the list I found this:

where I’m also involved!
I’m super excited to lead/join these interdisciplinary projects on Norwegian/Greenlandic fjords and climate change!
Yesterday the Bjerknes administration announced which of the “internal projects” they are to fund during the next four years – and I was very excited and happy to learn that our multi-disciplinary fjord project (led by Mari Myksvoll) was one of them!
Together with paleo-oceanographers and biologists, we will dive deep into the basins (and the mud/sediments) of Masfjorden to study how (and why) oxygen concentrations have varied in the “recent past” (the last 400yrs or so) and how that affects the ecosystem in the fjord.
I’m really looking forward to working locally – not only “locally” as in a nearby fjord, but also “locally” as in “together with colleagues in neighboring offices and buildings”! It’s is such a great team!

Well – don’t worry! Dr. Ruth Mottram, a Climate scientist at the Danish Meteorological Institute is on her way to the Greenland Ice sheet and she is bringing “Ice Man” and “Bat Girl” (likely friends of our Ninja) along! Read her cool story here! (The story “Ninja goes South” is still on Flickr.com!)

My lunch out in the sun ended abruptly when my husband (also in home office) casually asked if I’d heard about the new iceberg in the Weddell Sea. If my husband – an economist – has heard about an iceberg it’s likely to be big… so I shuffled the rest of my pancake into my mouth and ran in to read!
And yes, a quick google revealed that a huge chunk (4320 km2, to be precise) of the Ronne ice-shelf has broken off! A76, as it is called, is now the largest iceberg floating around Antarctica – but (according to NewScientist) it would not make it onto the top ten of historical giant icebergs.

It will be exciting to see where it drifts off to – and how it will influence the circulation on the continental shelf in the southern Weddell Sea. One of its old relatives, A23, that broke off from the neighboring Filchner ice-shelf in 1986, is still (!) stranded on the continental shelf, affecting e.g. the sea-ice distribution in the region.
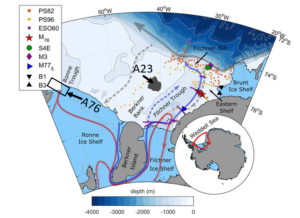
I’m now counting the days of what seems like an eternal quarantine, locked up alone in a hotel room in Bremerhafen, Germany. All alone – almost… Don’t tell anyone, but I’ve brought Mr. Ninja along, and he will join me when we fly off to Port Stanely and Polarstern in just over ten days! (Apparently the longest Lufthansa flight ever!) From Stanely, we will head south to the Weddell Sea, and hopefully recover the moorings we deployed in 2017.

If you’ve signed up to get e-mail alerts about new blog posts on the old website, you have to sign up again (to the right)! Sorry about that!
(and MANY thanks to Mirjam for helping me move!)